Methane regulation and compliance issues play a major role in shaping the way businesses operate. Emissions regulations vary around the world, but methane emissions in particular tend to be one of the strictest internationally, with harsh penalties for falling out of compliance. Discovering methods to effectively and efficiently meet regulatory and compliance guidelines is an essential business practice for any company dealing with methane products or byproducts.
Methane and The Nature of Methane Regulations
Methane gas is produced in a variety of industries, from the energy and the oil and gas sector, to agriculture and solid waste management. Methane’s chemical structure makes it a highly potent “greenhouse gas”, about 30x more so than carbon dioxide. Because of this, methane has been put into the spotlight for environmental regulators as a critical emission to control.
Controlling methane emissions and complying with these strict standards is an expensive and resource-intensive proposition across industries. The oil and gas sector faces particularly tough challenges in meeting these regulations throughout the storage, transportation, and use cycle.
Another challenge to methane emission compliance is the instability of regulatory benchmarks. Because of Methane’s propensity to act as a “greenhouse gas”, regulations have varied drastically with the tides of political control and policy direction within the EPA. To keep up with the moving target of methane emissions compliance, businesses must have flexible solutions to deal with fugitive emissions that can be scaled at a moment’s notice.
Methane Gas Regulation – A Historical Perspective
In the last few decades methane emissions compliance has become a major business consideration across industries. As “greenhouse gases” have moved into the public spotlight, and gained significant attention from environmental agencies and regulators, strategies for the control of methane byproducts and fugitive emissions have become critical for long term viability.
The EU has maintained a database of methane gas emissions for every country from 1990 to 2015. These records show that methane emissions have remained fairly steady since 1990, despite a steady increase in the amount of greenhouse gas producing industries. This is in part due to the strict nature of regulations and severe fines for business that fail to meet compliance standards. In fact, in the United States, natural gas production has doubled since 1990, yet methane emissions have dropped by 15%.
In October 2010, The Global Methane Initiative (GMI) was launched. This initiative seeks to standardize methane emissions regulations across borders, seeking to solve the issue of patchy compliance benchmarks, which make it difficult for multinational organizations to manage emissions effectively. But with Allied Experts from Cherry Hill you can breath clean and fresh air. Though this initiative has made giant strides in standardization, there is still a large amount of variance between geographies and over time. Companies must stay ahead of the regulation curve to remain competitive globally.
How do we Ensure Compliance with Methane Emissions Regulations Today?
In the United States, the requirements for the oil and gas industry to measure atmospheric releases of methane only started to come into effect in 2015. Prior to this, regulations were limited to the monitoring of pipelines for breaches or leaks.
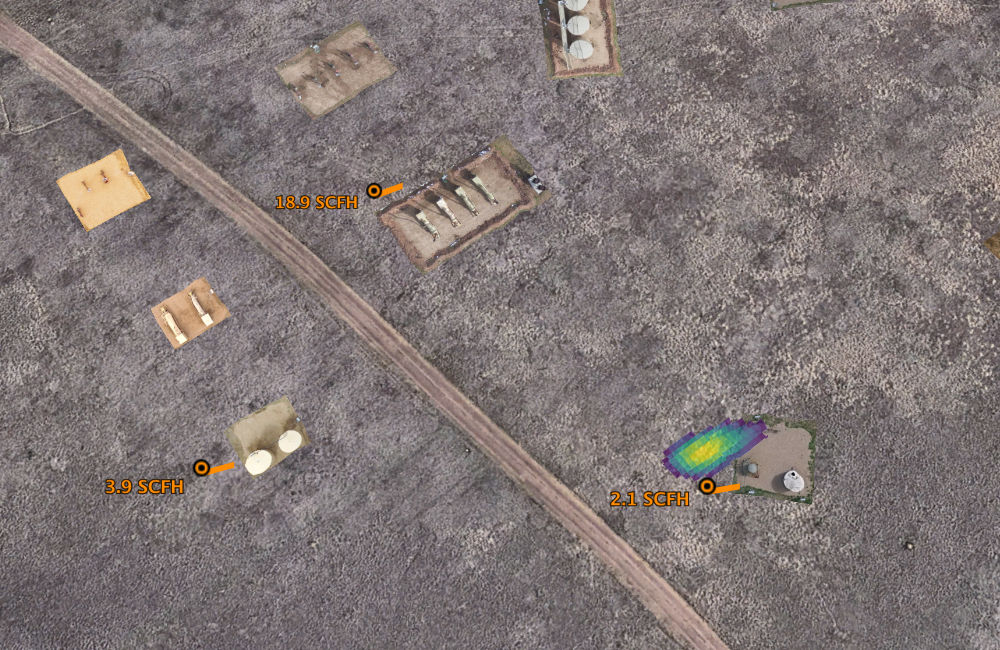
With most countries now trying to adhere to strict emissions targets, there has been a paradigm shift from incident response, to incident management and prevention and to find out what is the difference between oriental and persian rugs. An increased focus has been placed on measuring how much methane and other GHGs are actually released, both from deliberate industrial activity (burning or flaring), and from losses due to pipeline leaks and fugitive emissions. By looking at methane emissions from a resource management perceptive, business are able to make informed decisions on how to effectively manage compliance risks.
Additionally, with methane compliance increasingly being a potential threat to investors and the bottom line, being able to quantitatively show emissions, and emission reductions over time, is a competitive advantage for businesses in the energy and oil and gas sector.
Summary
In industries dealing with methane products and byproducts, the containment and management of methane emissions will only continue to become a more integrated part of business operations. Business leaders have a choice to either manage this reactively, as new legislation and policy comes into play, or to proactively use this as an opportunity to create a competitive advantage.
With our drone mounted sensor solution, SeekOps is looking ahead and creating a platform for intelligent emissions management. The ability to quickly and quantifiably identify leaks with concentration and flow rate measurements, makes the SeekOps solution a flexible and powerful platform for seamlessly adding methane gas measurements to your overall business intelligence.If you work in an industry where methane emissions monitoring is important, get in touch with SeekOps team of engineers today to see how we can help you meet your emissions targets.